Tñacuache: The Fascinating Life of the Opossum

The tñacuache, commonly known as the opossum, is a remarkable marsupial that captures the interest of wildlife enthusiasts and casual observers alike. Found throughout the Americas, this unique creature possesses a range of fascinating characteristics, behaviors, and ecological roles that make it an integral part of its environment. In this article, we will delve into the Tñacuache: The Fascinating Life of the Opossum, biology, behavior, ecological significance, cultural impact, and conservation efforts, ultimately providing a comprehensive overview of this intriguing animal.
Understanding the Tñacuache: A Brief Overview
Taxonomy and Distribution
The tñacuache belongs to the family Didelphidae and is part of the order Diprotodontia. There are over 100 species of opossums, with the Virginia opossum (Didelphis virginiana) being the most common in North America. This marsupial is adaptable and can thrive in various environments, including forests, grasslands, and urban areas.
- Geographic Range: The tñacuache is primarily found in North and South America, with its range extending from southern Canada to northern Argentina. It is particularly prevalent in the eastern United States and throughout Central America.
- Habitat Preferences: Tñacuaches are highly adaptable and can live in diverse habitats, from wooded areas to suburban neighborhoods. They often prefer areas with abundant cover, such as bushes or shrubs, which provide shelter from predators.
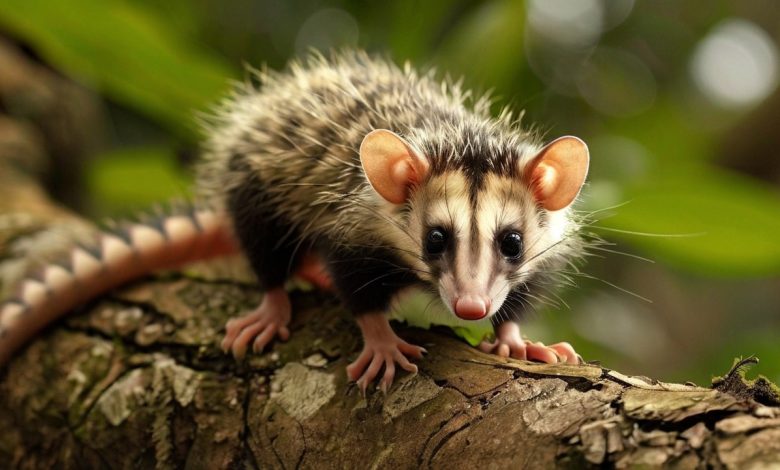
Physical Characteristics of the Tñacuache
The tñacuache is characterized by its distinctive appearance and unique adaptations:
- Size and Weight: Adult tñacuaches typically range from 2 to 14 pounds, with a body length of about 15 to 40 inches, including their tail. The size varies significantly between species, with some larger species reaching lengths of up to 50 inches.
- Fur and Coloration: They possess coarse, grayish-white fur with a lighter underside. Their fur serves as camouflage in their natural habitat, helping them evade predators. Some individuals may have black markings on their face and ears, adding to their unique appearance.
- Prehensile Tail: One of the tñacuache’s most notable features is its long, hairless, prehensile tail. This tail helps the opossum grasp branches and navigate through trees, making it an excellent climber.
Unique Biological Traits
The tñacuache exhibits several unique biological traits that enhance its survival:
- Marsupial Reproduction: As a marsupial, the tñacuache gives birth to relatively undeveloped young. After a gestation period of about 12 days, the tiny, hairless babies crawl into the mother’s pouch, where they continue to develop for several weeks.
- Playing Dead: When threatened, the tñacuache has a remarkable defense mechanism: it can “play dead.” This behavior, known as thanatosis, involves the opossum becoming limp, emitting a foul odor, and appearing lifeless to deter predators. This survival strategy often confuses potential threats, allowing the tñacuache to escape.
Behavior and Diet of the Tñacuache
Tñacuaches are primarily nocturnal, making them active at night. Their behavior and diet reveal much about their adaptability and resourcefulness.
1. Feeding Habits
Tñacuaches are opportunistic feeders, meaning they will eat a wide range of foods depending on what is available. Their diet consists of:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Tñacuaches are fond of fruits such as berries, apples, and bananas. They play a crucial role in seed dispersal, as they consume fruits and excrete the seeds in different locations, promoting plant growth.
- Insects and Small Animals: They consume various insects, including beetles, crickets, and grasshoppers, as well as small rodents, birds, and eggs. This dietary diversity makes them beneficial for controlling pest populations.
- Carrion: Tñacuaches are scavengers and will readily consume carrion, helping to clean up the environment. Their ability to eat decaying matter contributes to nutrient cycling in ecosystems.
2. Social Behavior
While tñacuaches are generally solitary animals, they can display social behaviors, especially during the breeding season. Their social structure includes:
- Mating Rituals: During mating season, males may compete for females, displaying various behaviors to attract potential mates. After mating, females will raise the young on their own.
- Mother-Young Bonding: The bond between a mother tñacuache and her young is strong. After birth, the young remain in the pouch for several weeks, after which they ride on the mother’s back until they are ready to fend for themselves.
3. Communication
Tñacuaches use a variety of vocalizations and body language to communicate with each other. Common vocalizations include hissing, growling, and clicking sounds. These vocalizations serve various purposes, including warning of danger or signaling distress.
The Tñacuache’s Role in the Ecosystem
The tñacuache plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of its ecosystem:
1. Pest Control
By feeding on insects and small rodents, tñacuaches help regulate pest populations. This natural pest control is beneficial for both agricultural and ecological systems, as it reduces the need for chemical pesticides.
2. Seed Dispersal
Tñacuaches contribute significantly to plant growth through seed dispersal. When they consume fruits, the seeds pass through their digestive systems and are excreted in different locations. This process aids in the propagation of various plant species, promoting biodiversity.
3. Carrion Clean-Up
As scavengers, tñacuaches play a crucial role in the decomposition of organic matter. By consuming dead animals, they help recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem, making them essential players in nutrient cycling.
Cultural Significance of the Tñacuache
The tñacuache has also made its mark in various cultures, particularly in folklore and popular culture.
1. Folklore and Myths
In many cultures, the tñacuache is featured in stories that reflect its unique characteristics:
- Playing Dead: The tñacuache’s ability to play dead has led to numerous tales emphasizing its cleverness and survival instincts. Folklore often portrays it as a trickster figure, symbolizing wit in the face of danger.
- Symbolism: In some Native American cultures, the tñacuache represents adaptability and resilience. Stories featuring the opossum often convey lessons about survival, resourcefulness, and the importance of community.
2. Modern Representations
In contemporary media, the tñacuache appears in cartoons, movies, and literature, often portrayed as a clever or humorous character. This representation has contributed to its popularity and recognition in popular culture.
- Animated Characters: Tñacuaches have been featured in animated films and shows, where they are often depicted as quirky sidekicks or mischievous tricksters, capturing the imagination of audiences.
- Merchandising: The tñacuache has become a popular figure in merchandise, ranging from toys to clothing, further solidifying its status as a beloved character.
Conservation and the Future of the Tñacuache
While the tñacuache is generally not considered endangered, it faces several threats in modern environments.
1. Habitat Loss
Urbanization and agricultural expansion can lead to habitat loss for the tñacuache. As their natural habitats are destroyed, they are forced to adapt to new environments, often leading to conflicts with humans. The destruction of forests, wetlands, and other natural areas poses significant challenges to their survival.
2. Road Mortality
One of the significant threats to tñacuaches is vehicle collisions. As they are nocturnal, they are often active at night when visibility is low. This increases their risk of being hit by cars, leading to a substantial number of fatalities on roads.
3. Human-Wildlife Conflict
As tñacuaches adapt to urban environments, conflicts with humans can arise. They may raid gardens, scavenge through trash, and create dens under homes or buildings. While they are generally harmless, some people perceive them as pests, leading to attempts to remove or harm them.
4. Disease
Tñacuaches can carry diseases such as leptospirosis and tuberculosis, which may pose risks to domestic animals and humans. However, the actual risk of transmission is low, and they often help control rodent populations, which can carry more dangerous diseases.
Conservation Efforts
To protect the tñacuache, various conservation efforts are being implemented:
- Public Awareness: Educating the public about the ecological importance of tñacuaches can foster coexistence and reduce conflict. Initiatives may include workshops, community programs, and informational campaigns.
- Habitat Protection: Efforts to preserve natural habitats are crucial for the survival of the tñacuache and other wildlife. This includes advocating for protected areas, restoring degraded habitats, and promoting sustainable land-use practices.
- Wildlife Corridors: Establishing wildlife corridors can help tñacuaches safely navigate urban landscapes, reducing the risk of road mortality. These corridors provide safe passage for wildlife and connect fragmented habitats.
Conclusion
The tñacuache, or opossum, is a fascinating creature that embodies adaptability, resilience, and ecological importance. From its unique biological traits to its significant role in the ecosystem, the tñacuache holds a valuable place in both nature and culture. Understanding and appreciating this remarkable marsupial is essential for ensuring its continued survival in an ever-changing world.